South Australian Medical Heritage Society Inc
Website for the Virtual Museum
Home
Coming meetings
Past meetings
About the Society
Main Galleries
Medicine
Surgery
Anaesthesia
X-rays
Hospitals,other organisations
Individuals of note
Small Galleries
Ethnic medicine
- Aboriginal
- Chinese
- Mediterran
Serum biochemistry then and now
Acknowledgments:
This contribution has been stimulated by Dr. Roy Francis who contacted us about his collection of interesting medical items. Dr. Francis has been a solo general practitioner at Snowtown in South Australia (1970-1994) and was very keen to provide total patient care.
Before the arrival of fax he was one of the first to use the Cardiophon,e a telephone link to send an ECG to the cardiologists in Adelaide using two telephone lines. He also purchased biochemical and haematological apparatus to screen his patients with diagnostic or pre-operative tests. The following photographs show some of the apparatus used by him in Snowtown.
Photographs of recent biochemistry apparatus and some early biochemistry items (1950s) have been kindly provided by Neil Pascoe, senior scientist in the Department of Clinical Chemistry at The Queen Elizabeth Hospital .

A recent photograph of a biochemistry laborarory at The Queen Elizabeth Hospital.


Unimeter 250. An early machine used to measure blood glucose, haemoglobin and cholesterol, used by Dr. Francis in Snowtown (left).
A standard centrifuge which separated red cells from serum (right).
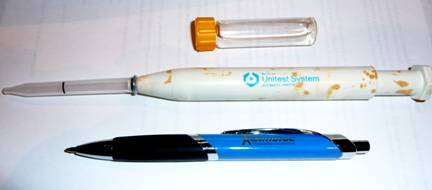
After standardising the apparatus with a control sample, an appropriate reagent was placed in the cuvette (above). A pipette was then used to draw up the serum sample to the black mark, mixed with the reagent and placed in the well of the Unimeter. The values can then be seen on the scale. A ballpoint pen is shown to indicate the size.


An early apparatus to measure serum albumin in the urine, attributed to the French physician Dr. Esbach. The divisions relate to the albumin value.

Apparatus to determine blood ammonia, called the Conney flask

A later model Unimeter 300. It could measure more than 10 serum values. Different cards were inserted under the window (top right) to measure specific serum components.

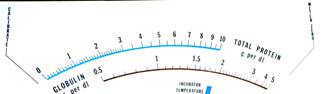


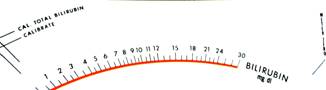
Samples of the changeable cards, used to determine the base line (standards) and to measure blood levels of protein, globulin, phosphate, alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin.

A coagulation analyser used by Dr. Francis to monitor his patients who were on warfarin, an anticoagulant.


Front and back views of a “comparometer” used in the 1950s. The principle is similar to the Sahli haemoglobinometer. A standard solution is placed in a cuvette (top right) the tested sample is placed in another cuvette. A diluting solution is added until the colours match. The volume of the diluting solution indicates the concentration of the tested sample. This is read on a provided chart.
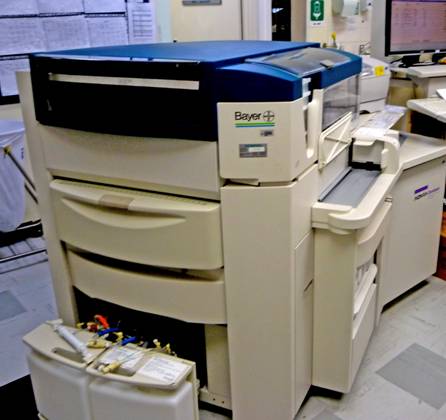

Radioimmunoassay machine. It is used in research to detect blood concentrations of drugs. It can also measure concentrations of specific molecules such as insulin and thyroid hormones. It can also detect and monitor specific tumour markers for cancer of the prostate (PSA) and colon (CEA). The automation is a major labour saving.



Multiple serum biochemistry analyser. More than 30 analytes can be measured the top picture shows the machine acquiring a sample of serum,
The further photographs show the machine acquiring a sample of serumand then transferring the samples, adding reagents and calculating the samples, adding the reagents and calculating the values for a particular blood chemical. To prevent contamination from the next sample, a through rinse is required. The machine uses 60 litres of pure water each hour.

Cobas 411 immuno analyser. It detects lower quantaties of specific blood components such as Troponin, a molecule associated with heart muscle damage, vitamin b12, serum HCG which is elevated in pregnancy, and other low concentration hormones.
-o0o-